SpringBoot-整合篇
整合篇包含SpringBoot对各种第三方技术的整合。例如SQL、NoSQL、缓存、消息队列、定时任务、文档操作、认证授权、消息通知等等
1.整合SQL
①MyBatis
步骤①:导入 MyBatis 的 starter 和对应数据库的坐标,或者创建项目时勾选要使用的技术
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
|
步骤②:配置数据源相关信息,没有这个信息你连接哪个数据库都不知道
1
2
3
4
5
6
| spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_db?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: root
|
测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| SET NAMES utf8;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `tbl_book`;
CREATE TABLE `tbl_book` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(50) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`type` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`description` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (1, '三体', '科幻', '大刘的巅峰之作,将中国科幻推向世界舞台。总共分为三部曲:《地球往事》、《黑暗森林》、《死神永生》。');
INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (2, '格林童话', '童话', '睡前故事。');
INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES (3, 'Spring 5设计模式', '计算机理论', '深入Spring源码剖析Spring源码中蕴含的10大设计模式');
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public class Book {
private Integer id;
private String type;
private String name;
private String description;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
| @Mapper
public interface BookDao {
@Select("select * from tbl_book where id = #{id}")
public Book getById(Integer id);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @SpringBootTest
class Springboot05MybatisApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(bookDao.getById(1));
}
}
|
总结
- 整合操作需要勾选MyBatis技术,也就是导入MyBatis对应的starter
- 数据库连接相关信息转换成配置
- 数据库SQL映射需要添加@Mapper被容器识别到
- MySQL 8.X驱动强制要求设置时区
- 修改url,添加serverTimezone设定
- 修改MySQL数据库配置:修改mysql中的配置文件mysql.ini,在mysqld项中添加default-time-zone=+8:00
- 驱动类过时,提醒更换为com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
②MyBatis-Plus
步骤①:导入对应的 starter 和数据库驱动
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| <dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
|
步骤②:配置数据源相关信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
| spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_db
username: root
password: root
|
步骤③:配置表名的通用前缀名
数据库的表名定义规则是tbl_模块名称,为了能和实体类相对应,需要设置所有表名的通用前缀名
1
2
3
4
| mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
table-prefix: tbl_
|
步骤④:配置运行日志
通过配置运行日志就可以查阅执行时的SQL语句
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
table-prefix: tbl_
id-type: auto
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
|
测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public class Book {
private Integer id;
private String type;
private String name;
private String description;
}
|
1
2
3
| @Mapper
public interface BookDao extends BaseMapper<Book> {
}
|
核心在于Dao接口继承了一个BaseMapper的接口,这个接口中帮助开发者预定了若干个常用的API接口,简化了通用API接口的开发工作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @SpringBootTest
class SpringbootApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(bookDao.selectById(2));
System.out.println(bookDao.selectList(null));
}
}
|
总结
- 手工添加MyBatis-Plus对应的starter
- 数据层接口使用BaseMapper简化开发
- 借助MyBatis-Plus日志可以查阅执行SQL语句
- 需要使用的第三方技术无法通过勾选确定时,需要手工添加坐标
③Durid
前面整合 MyBatis 和 MyBatis-Plus 的时候,使用的数据源对象都是SpringBoot默认的数据源对象 HiKari,下面我们手工控制一下,自己指定了一个数据源对象 Druid。
步骤①:导入对应的starter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
步骤②:修改配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| spring:
datasource:
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_db?serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: root
|
总结
- 整合Druid需要导入Druid对应的starter
- 根据Druid提供的配置方式进行配置
2.整合NoSQL
①Redis
步骤①:导入对应的 starter 和依赖
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
步骤②:修改配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| spring:
redis:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
password: 123456
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 8
max-idle: 8
min-idle: 0
max-wait: 100ms
|
步骤③:使用springboot整合redis的专用客户端接口操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| @SpringBootTest
class SpringRedisApplicationTests {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void testString() {
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
ops.set("name","jianjian");
String name = (String) ops.get("name");
System.out.println("name = " + name);
}
}
|
由于redis内部不提供java对象的存储格式,因此当操作的数据以对象的形式存在时,会进行转码,转换成字符串格式后进行操作。为了方便开发者使用基于字符串为数据的操作,springboot整合redis时提供了专用的API接口StringRedisTemplate,可以理解为这是RedisTemplate的一种指定数据泛型的操作API。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @SpringBootTest
public class StringRedisTemplateTest {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Test
void get(){
ValueOperations ops = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
String name = ops.get("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
}
|
redis客户端选择
springboot整合redis技术提供了多种客户端兼容模式,默认提供的是lettuce客户端技术,也可以根据需要切换成指定客户端技术,例如jedis客户端技术,切换成jedis客户端技术操作步骤如下:
步骤①:导入jedis坐标
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
步骤②:配置客户端技术类型,设置为jedis
1
2
3
4
5
| spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
client-type: jedis
|
步骤③:根据需要设置对应的配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
client-type: jedis
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 16
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 16
|
lettcus与jedis区别
- jedis连接Redis服务器是直连模式,当多线程模式下使用jedis会存在线程安全问题,解决方案可以通过配置连接池使每个连接专用,这样整体性能就大受影响
- lettcus基于Netty框架进行与Redis服务器连接,底层设计中采用StatefulRedisConnection。 StatefulRedisConnection自身是线程安全的,可以保障并发访问安全问题,所以一个连接可以被多线程复用。当然lettcus也支持多连接实例一起工作
②ElasticSearch
步骤①:导入对应的依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
步骤②:修改配置
1
2
3
| elasticsearch:
cluster-name: my-application
cluster-nodes: 127.0.0.1:9200
|
③MongoDB
3.整合消息队列
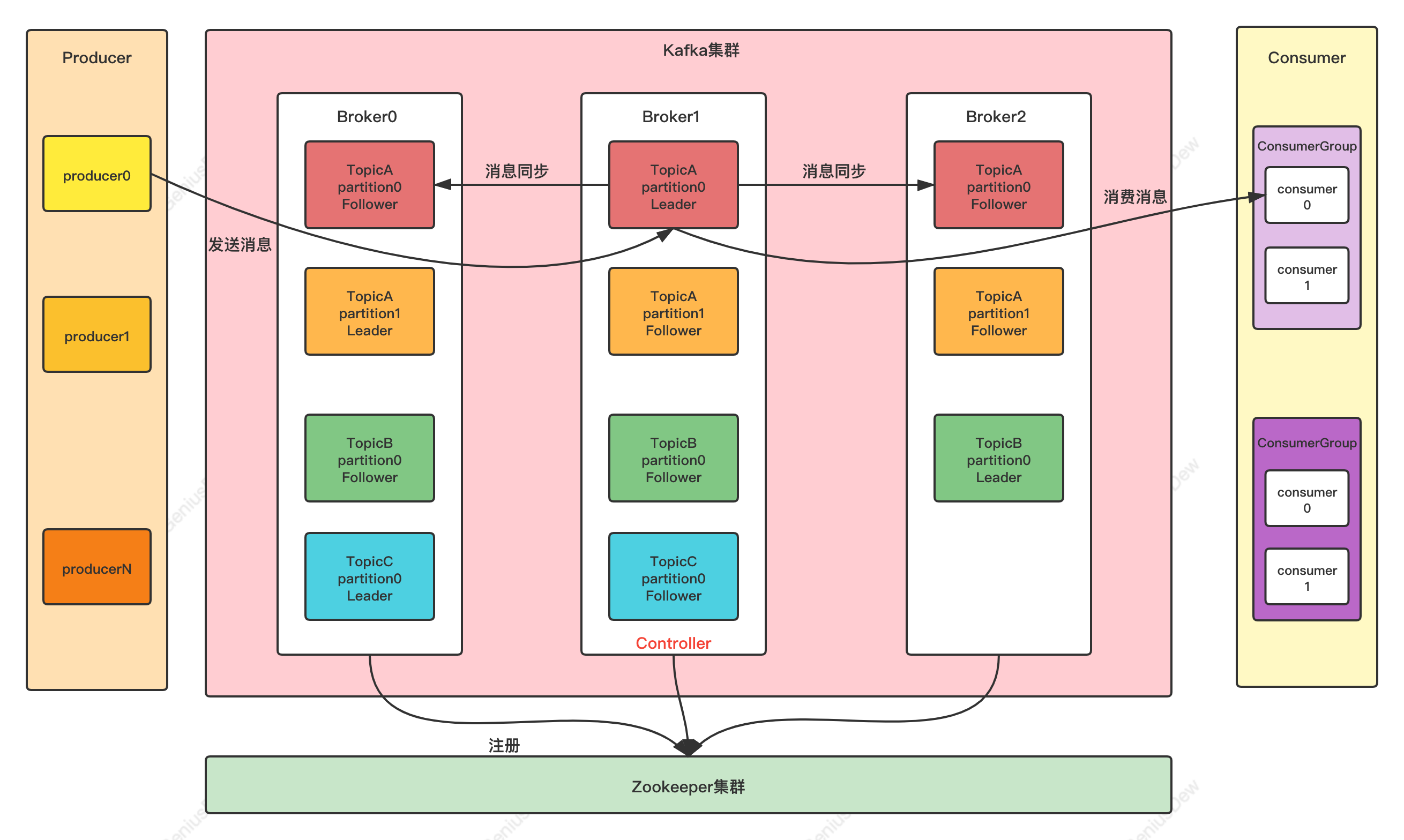
①kafka

| 概念 |
解释 |
| Broker |
节点,一个Broker代表是一个Kafka实例节点,多个Broker可以组成Kafka集群 |
| Topic |
主题,等同于消息系统中的队列(queue),一个Topic中存在多个Partition |
| Partition |
分区,构成Kafka存储结构的最小单位 |
| Partition offset |
offset为消息偏移量,以Partition为单位,即使在同一个Topic中,不同Partition的offset也是重新开始计算(也就是会重复) |
| Group |
消费者组,一个Group里面包含多个消费者 |
| Message |
消息,是队列中消息的承载体,也就是通信的基本单位,Producer可以向Topic中发送Message |
❶下载并启动
下载地址:https://kafka.apache.org/downloads
运行以下命令以正确的顺序启动所有服务:
1
2
|
$ bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh config/zookeeper.properties
|
打开另一个终端会话并运行:
1
2
|
$ bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties
|
成功启动所有服务后,您将拥有一个基本的 Kafka 环境运行并可供使用。
❷引入依赖并配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
<version>3.0.6</version>
</dependency>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| sping:
kafka:
bootstrap-servers: localhost:9092
consumer:
group-id: my-group
auto-offset-reset: earliest
producer:
value-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
key-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
|
❸生产者发送消息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @Component
class KafkaProducer {
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate kafkaTemplate;
public void sendMessage(String topic, String content) {
kafkaTemplate.send(topic, content);
}
}
|
❹消费者接收消息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Component
class KafkaConsumer {
@KafkaListener(topics = {"test"})
public void handleMessage(ConsumerRecord record) {
System.out.println(record.value());
}
}
|
❺测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| @SpringBootTest
public class KafkaTests {
@Autowired
private KafkaProducer kafkaProducer;
@Test
public void testKafka() {
kafkaProducer.sendMessage("test", "你好");
kafkaProducer.sendMessage("test", "在吗");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000 * 10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
②RabbitMQ
❶安装RabbitMQ
1
| docker pull rabbitmq:3-management
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| docker run \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=jianjian \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=123321 \
--name mq \
--hostname mq1 \
-p 15672:15672 \
-p 5672:5672 \
-d rabbitmq:3-management
|
访问 http://127.0.0.1:15672 即可
❷引入依赖并配置
导入springboot整合amqp的starter,amqp协议默认实现为rabbitmq方案
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
配置RabbitMQ的服务器地址
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 5672
virtual-host: /
username: jianjian
password: 123321
|
案例
- 利用@RabbitListener声明Exchange、Queue、RoutingKey
- 在consumer服务中,编写两个消费者方法,分别监听direct.queue1和direct.queue2
- 在publisher中编写测试方法,向jianjian. direct发送消息
❸消息接收(direct)
在consumer的SpringRabbitListener中添加两个消费者,同时基于注解来声明队列和交换机:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| @Component
public class SpringRabbitListener {
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue1"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "jianjian.direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
key = {"red", "blue"}
))
public void listenDirectQueue1(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者接收到direct.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue2"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "jianjian.direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
key = {"red", "yellow"}
))
public void listenDirectQueue2(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者接收到direct.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
}
|
❹消息发送(direct)
在publisher服务中添加测试方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @SpringBootTest
public class SpringAmqpTest {
@Test
public void testSendDirectExchange() {
String exchangeName = "jianjian.direct";
String message = "红色警报!日本乱排核废水,导致海洋生物变异,惊现哥斯拉!";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "red", message);
}
}
|
③RocketMQ
4.整合定时任务
①Quartz
Quartz技术是一个比较成熟的定时任务框架。springboot对其进行整合后,简化了一系列的配置,将很多配置采用默认设置,这样开发阶段就简化了很多。
Quartz相关概念
- 工作(Job):用于定义具体执行的工作
- 工作明细(JobDetail):用于描述定时工作相关的信息
- 触发器(Trigger):用于描述触发工作的执行规则,通常使用cron表达式定义规则
- 调度器(Scheduler):描述了工作明细与触发器的对应关系
简单说就是你定时干什么事情,这就是工作;工作不可能就是一个简单的方法,还要设置一些明细信息;工作啥时候执行,设置一个触发器;工作和触发器都是独立定义的,它们两个怎么配合到一起呢?用调度器。
步骤①:导入springboot整合Quartz的starter
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-quartz</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
步骤②:定义任务Bean,按照Quartz的开发规范制作,继承QuartzJobBean
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public class MyQuartz extends QuartzJobBean {
@Override
protected void executeInternal(JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException {
System.out.println("quartz task run...");
}
}
|
步骤③:创建Quartz配置类,定义工作明细(JobDetail)与触发器的(Trigger)bean
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| @Configuration
public class QuartzConfig {
@Bean
public JobDetail printJobDetail(){
return JobBuilder.newJob(MyQuartz.class).storeDurably().build();
}
@Bean
public Trigger printJobTrigger(){
ScheduleBuilder schedBuilder = CronScheduleBuilder.cronSchedule("0/5 * * * * ?");
return TriggerBuilder.newTrigger().forJob(printJobDetail()).withSchedule(schedBuilder).build();
}
}
|
工作明细中要设置对应的具体工作,使用newJob()操作传入对应的工作任务类型即可。
触发器需要绑定任务,使用forJob()操作传入绑定的工作明细对象。此处可以为工作明细设置名称然后使用名称绑定,也可以直接调用对应方法绑定。
触发器中最核心的规则是执行时间,此处使用调度器定义执行时间,执行时间描述方式使用的是cron表达式。
cron表达式详解
在spring 4.x中已经不支持7个参数的cron表达式了,要求必须是6个参数。cron表达式格式如下:
1
| {秒} {分} {时} {日期(具体哪天)} {月} {星期}
|
-
秒:必填项,允许的值范围是0-59,支持的特殊符号包括
,
,表示特定的某一秒才会触发任务-表示一段时间内会触发任务*表示每一秒都会触发/表示从哪一个时刻开始,每隔多长时间触发一次任务。
-
分:必填项,允许的值范围是0-59,支持的特殊符号和秒一样,含义类推
-
时:必填项,允许的值范围是0-23,支持的特殊符号和秒一样,含义类推
-
日期:必填项,允许的值范围是1-31,支持的特殊符号相比秒多了?,表示与{星期}互斥,即意味着若明确指定{星期}触发,则表示{日期}无意义,以免引起冲突和混乱。
-
月:必填项,允许的值范围是1-12 (JAN-DEC),支持的特殊符号与秒一样,含义类推
-
星期:必填项,允许值范围是1~7 (SUN-SAT),1代表星期天(一星期的第一天),以此类推,7代表星期六,支持的符号相比秒多了?,表达的含义是与{日期}互斥,即意味着若明确指定{日期}触发,则表示{星期}无意义。
总结
- springboot整合Quartz就是将Quartz对应的核心对象交给spring容器管理,包含两个对象,JobDetail和Trigger对象
- JobDetail对象描述的是工作的执行信息,需要绑定一个QuartzJobBean类型的对象
- Trigger对象定义了一个触发器,需要为其指定绑定的JobDetail是哪个,同时要设置执行周期调度器
②Task
Spring Task是Spring 3.0自带的定时任务,可以将它看作成一个轻量级的Quartz,功能虽然没有Quartz那样强大,但是使用起来非常简单,无需增加额外的依赖,可直接上手使用。
步骤①:开启定时任务功能,在引导类上开启定时任务功能的开关,使用注解@EnableScheduling
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @SpringBootApplication
@EnableScheduling
public class SpringbootTaskApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot22TaskApplication.class, args);
}
}
|
步骤②:定义Bean,在对应要定时执行的操作上方,使用注解@Scheduled定义执行的时间,执行时间的描述方式还是cron表达式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Component
public class MyBean {
@Scheduled(cron = "0/1 * * * * ?")
public void print(){
System.out.println("spring task run...");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
|
步骤③:如何想对定时任务进行相关配置,可以通过配置文件进行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| spring:
task:
scheduling:
pool:
size: 1
thread-name-prefix: ssm_
shutdown:
await-termination: false
await-termination-period: 10s
|
总结
- spring task需要使用注解@EnableScheduling开启定时任务功能
- 注解@Scheduled为定时执行的的任务设置执行周期,描述方式cron表达式
5.整合认证授权
①Spring Security
②Shiro
③Oauth2
6.整合文档操作
①PDF
②Word
③Excel
④上传下载
7.整合通知
①邮件
②钉钉
③微信
④短信